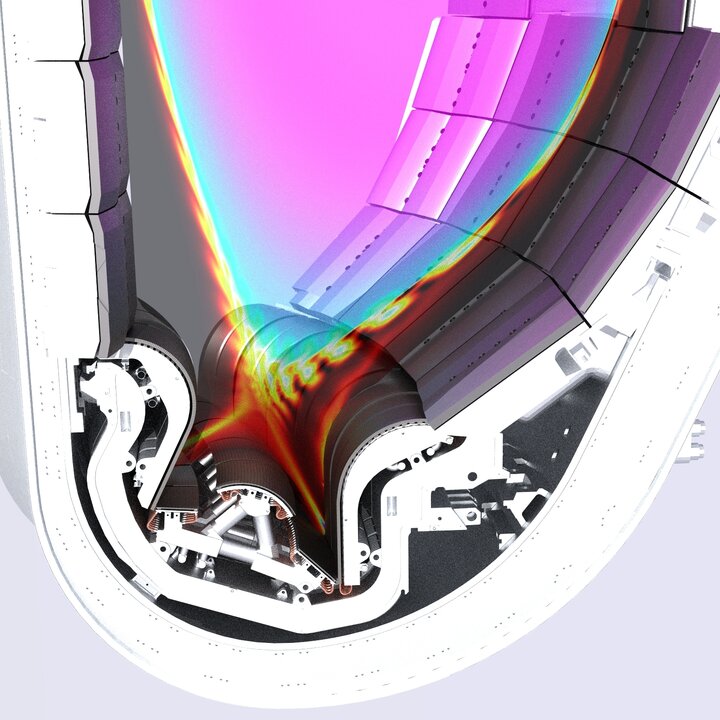
Simulations of instabilities in fusion plasmas, developing the predictive capability for their occurrence, consequences and control, are required for the preparation of operation of ITER and design of future machines
Fusion plasmas can suffer from global instabilities of the magnetic structure of the plasma. The so-called magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instabilities, driven unstable by the plasma pressure and current, can cause fast losses of the thermal plasma energy. A typical time scale is of the order of 100ms to 1ms.
Read moreRecent Publications
Our most recent peer reviewed publications
-
S.Q. Korving,G.T.A. Huijsmans,J.-S. Park,A. Loarte
Development of the neutral model in the nonlinear MHD code JOREK
Physics of Plasmas (2023) -
Ashish Bhole,Boniface Nkonga,Stanislas Pamela,Guido Huijsmans,Matthias Hoelzl
Treatment of polar grid singularities in the bi-cubic Hermite-Bézier approximations
Journal of Computational Physics (2022) -
S.K. Kim,S. Pamela,N. Logan,Y.S. Na,C. Lee,J.K. Park,S. Yang,Q. Hu,M. Becoulet,G. Huijsmans
Nonlinear MHD modeling of n = 1 RMP-induced pedestal transport and mode coupling effects on ELM suppression in KSTAR
Nuclear Fusion (2022) -
T.J. Bogaarts,M. Hoelzl,G.T.A. Huijsmans,X. Wang
Development and application of a hybrid MHD-kinetic model in JOREK
Physics of Plasmas (2022) -
G. F-Torija Daza,J.M. Reynolds-Barredo,R. Sanchez,A. Loarte,G. Huijsmans
Free-plasma-boundary solver for axisymmetric ideal MHD equilibria with flow
Nuclear Fusion (2022)