High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) is a novel imaging modality that creates new opportunities for bone research. Its high resolution allows detailed in vivo visualization and three-dimensional reconstruction of the cortex and trabeculae of peripheral bones as well as quantification of total, cortical, and trabecular geometry, density, and microarchitecture. It can also be used to calculate peripheral bone strength with finite element analysis. Today, HR-pQCT is being used for various clinical applications, including for example bone microarchitectural and strength assessments in patients with osteoporosis, fracture risk prediction, and more recently the application in distal radius fracture healing and rheumatoid arthritis-affected finger joints.
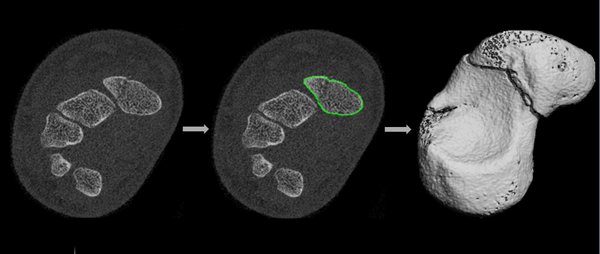
Other clinical applications may also benefit from HR-pQCT imaging, such as the scaphoid bone, a small bone in the carpus, for the diagnosis of scaphoid fractures. These fractures are the most common carpal bone fractures but difficult to diagnose with current imaging modalities. HR-pQCT could possibly also be used to study the healing of these fractures. Besides that, HR-pQCT may provide new insights into diseases other than osteoporosis, such as rare metabolic bone disorders.
This project investigates novel applications of HR-pQCT. The first aim is to study the effects of calcium and/or vitamin D supplementation on distal radius fracture healing in an intervention study following up our recent studies on HR-pQCT in distal radius fracture healing. The second aim is to explore the application of HR-pQCT imaging of the scaphoid bone in patients with a clinically suspected scaphoid fracture (see figure) and to compare the diagnostic performance of HR-pQCT to conventional CT. Additionally, HR-pQCT is used to study the healing of scaphoid fractures and to evaluate the association between bone shape and fracture occurrence. The third and last aim is to apply HR-pQCT in patients with rare metabolic bone disorders and to assess bone microarchitecture and strength.