Fundamentals of the Nonlinear Optical Channel
The FUN-NOTCH project copes foundational questions around the emerging phenomena of transceivers operated near the nonlinear regime of fibers. We aim at approaching theoretical mechanisms to optimize the current technologies, and we expect this will positively contribute to extending the capacity crunch in optical fiber communications.
Duration
January 2018 - June 2023Project Manager
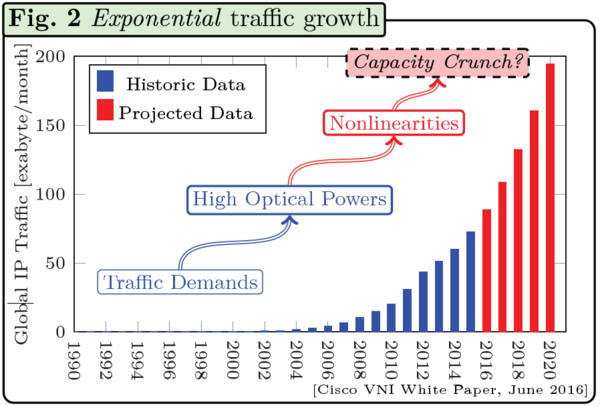
Fibre optics are critical infrastructure for society because they carry nearly all the global Internet traffic. For a long time, optical fibre systems were thought to have infinite information-carrying capabilities. With current traffic demands growing by a factor between 10 and 100 every decade, however, this is no longer the case. In fact, it is currently unknown if the installed optical infrastructure will manage to cope with these demands in the future, or if we will face the so-called “capacity crunch”.
To satisfy traffic demands, transceivers are being operated near the nonlinear regime of the fibres. In this regime, a power-dependent nonlinear phenomenon known as the Kerr effect becomes the key impairment that limits the information-carrying capability of optical fibres. The intrinsic nonlinear nature of these fibres makes the analysis very difficult and has led to a series of unanswered fundamental questions about data transmission in nonlinear optical fibres, and nonlinear media in general. For example, the maximum amount of information that optical fibres can carry in the highly nonlinear regime is still unknown, and the design of transceivers well-suited for this regime is also completely unexplored. These fundamental questions are the key objective of this project which will ultimately give an answer to the capacity crunch question.
Participants
Project Related Publications
-
Sebastiaan Goossens,Yunus Can Gultekin,Olga Vassilieva,Inwoong Kim,Paparao Palacharla,Chigo Okonkwo,Alex Alvarado
Introducing 4D Geometric Shell Shaping for Mitigating Nonlinear Interference Noise
Journal of Lightwave Technology (2023) -
Yunus Can Gültekin,Frans M.J. Willems,Alex Alvarado
Band-ESS
(2023) -
Viswanathan Ramachandran,Gabriele Liga,Astrid Barreiro,Alex Alvarado
Capacity Region Bounds for Optical WDM Channels based on First-Order Regular Perturbation
Journal of Lightwave Technology (2023) -
Kaiquan Wu,Gabriele Liga,Jeffrey Lee,Alex Alvarado
DFE State-Tracking Demapper for Soft-Input FEC in 800G Data Center Interconnects
(2022) -
Astrid Barreiro,Gabriele Liga,Alex Alvarado
A Data-driven optimization of First-order Regular Perturbation Coefficients for Fiber Nonlinearities
(2022)
Fibre optics are critical infrastructure for society because they carry nearly all the global Internet traffic. For a long time, optical fibre systems were thought to have infinite information-carrying capabilities. With current traffic demands growing by a factor between 10 and 100 every decade, however, this is no longer the case. In fact, it is currently unknown if the installed optical infrastructure will manage to cope with these demands in the future, or if we will face the so-called “capacity crunch”.
To satisfy traffic demands, transceivers are being operated near the nonlinear regime of the fibres. In this regime, a power-dependent nonlinear phenomenon known as the Kerr effect becomes the key impairment that limits the information-carrying capability of optical fibres. The intrinsic nonlinear nature of these fibres makes the analysis very difficult and has led to a series of unanswered fundamental questions about data transmission in nonlinear optical fibres, and nonlinear media in general. For example, the maximum amount of information that optical fibres can carry in the highly nonlinear regime is still unknown, and the design of transceivers well-suited for this regime is also completely unexplored. These fundamental questions are the key objective of this project which will ultimately give an answer to the capacity crunch question.
Our Partners
Researchers involved in this project
Project description
To satisfy traffic demands, transceivers are being operated near the nonlinear regime of the fibres. In this regime, a power-dependent nonlinear phenomenon known as the Kerr effect becomes the key impairment that limits the information-carrying capability of optical fibres. The intrinsic nonlinear nature of these fibres makes the analysis very difficult and has led to a series of unanswered fundamental questions about data transmission in nonlinear optical fibres, and nonlinear media in general. For example, the maximum amount of information that optical fibres can carry in the highly nonlinear regime is still unknown, and the design of transceivers well-suited for this regime is also completely unexplored. These fundamental questions are the key objective of this project which will ultimately give an answer to the capacity crunch question.
Research Output
If you are interested in learning more about this project, an overview of publications can be found here
